Taylor and Jim Metzler of Webtorials
explain it, a common approach to de-
signing a branch office WAN is to have
T1-based access to a service providers
MPLS network at each branch office
plus one or more high-speed links at
each data center. It is not uncommon
in this design for a company’s Internet
traffic to be backhauled to a data center
before being handed off to the Internet.
In other words, the Internet-bound traf-
fic transits both the MPLS network and
the Internet access link, adding both
cost and delay.
“The penalties associated with
backhauling Internet traffic are usually
acceptable if the amount of Internet
traffic is relatively light,” write the
Webtorials analysts. “However, the
Internet traffic generated by most com-
panies is large and growing.”
Again, while MPLS provides a
highly stable, high-performance, and
highly scalable means of intercon-
necting multiple data centers and
branch offices, it can be expensive,
and the expense makes the most
sense when applications were largely
hosted in data centers and the Inter-
net could not deliver business-grade
reliability. Today, applications increas-
ingly are offered on-demand, via the
Internet and cloud, and SD-WAN, as
a virtual overlay, adds security and
reliability to lower-cost broadband
connections, say its proponents. One
upshot can be a reduced dependency
on MPLS connections.
That’s not to say SD-WAN elimi-
nates the need for MPLS, at least not
in most cases. What SD-WAN does
do is bond and support multiple WAN
access technologies, such as DSL,
LTE, leased lines, MPLS VPN, etc.
It creates overlay tunnels on top of
available transports links that make
up an organization’s WAN, while edge
devices at customer sites allow IT ad-
ministrators to manage or automate,
via centralized policies, WAN function-
ality, including configuration, provision-
ing and security. Users should also
be able to dynamically set the path
for each application based on their
customer-defined policies.
It’s a benefit that can’t be under-
estimated as hybrid WAN topologies
become the norm. According to one
survey by Forrester, for instance, 54
percent of network and telecom man-
agers are dealing with four or more
connection technologies within their
networks, from private leased lines to
carrier Ethernet to 4G/LTE to MPLS
to terrestrial fixed wireless. More than
three-quarters of firms use more than
one, so anything that streamlines man-
agement, orchestration and mainte-
nance could be seen as a boon.
There is a related business case,
as well. Network managers can push
less-critical, non-real-time data onto
less expensive, best-efforts links,
while reserving more expensive,
dedicated links for mission-critical and
real-time data.
That’s also where MPLS comes in
(or in the case of our mixed topology,
remains in). With MPLS WAN technol-
ogy, users have full control over traffic
engineering. The intelligence in SD-
WAN lies on the edge, via boxes on
the customer premises that are con-
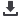
Source: Silver Peak Systems
Per
TeleGeography.com- Broadband vs. MPLS pricing for San Francisco Q4 2014. Median monthly price:
10-20 Mbps Broadband $110/month, 10Mbps MPLS IP VPN + Local Access $2,100 Month.
Source: Telstra
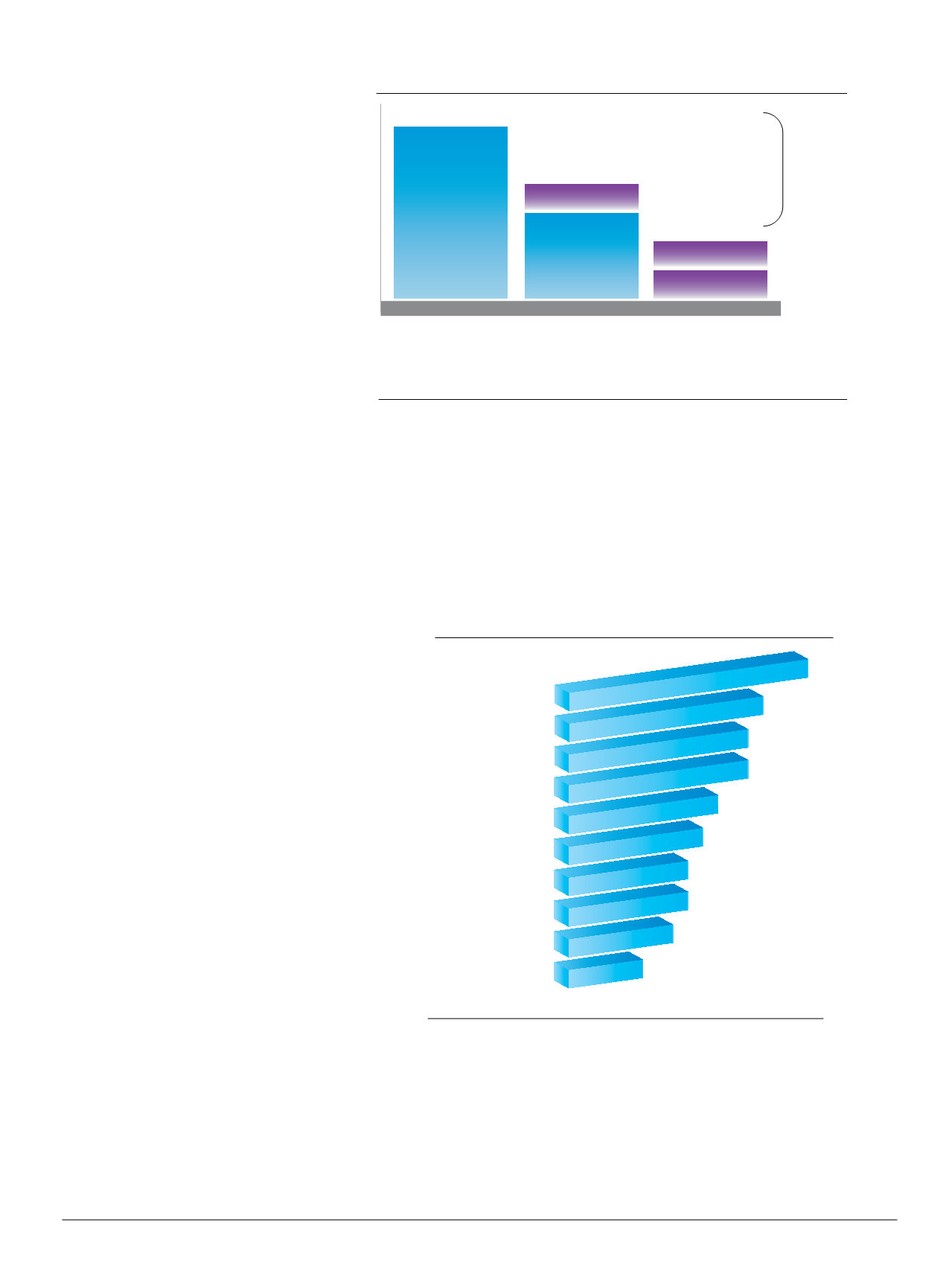
Potential Cost Savings from SD-WAN
Example Managed SD-WAN Solution
Source: Webtorials
What are the primary advantages that would drive
your company to implement an SD-WAN?
Increase flexibility
Reduce OPEX
Improve application performance
Simplify operations
Improve security
Improve availability
Deploy new functionality more quickly
Add bandwidth more quickly
Provide better visibility
Reduce CAPEX
MPLS - 10Mbps
~$2100/Month
MPLS only
~$2,520,000
Hybrid
~$1,200,000
Dual Internet
~$264,000
~$1100/Month
~$220/Month
Up to 90%
reduction
in WAN
costs
Internet 10 Mbps
MPLS - 5Mbps
Internet 10 Mbps
Internet 10 Mbps
Monthly Cost Per Site
Cost Per Year for 100 Sites
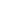
OFFICE BRANCH
APPLICATION
TRAFFIC
APPLICATION
ACCELERATION
ROUTER
FIREWALL
INTERNET
IP VPN
DATA CENTER
IP
16%
13%
12%
12%
10%
9%
8%
8%
7%
5%
0% 2% 4% 6% 8% 10% 12% 14% 16%
Source: Silver Peak Systems
Per
TeleGeography.com- Broadband vs. MPLS pricing for San Francisco Q4 2014. Median monthly price:
10-20 Mbps Broadband $110/month, 10Mbps MPLS IP VPN + Local Access $2,100 Month.
Source: Telstra
Over the next 5 years, hosted VoIP and
UC will be the seg ent with the largest
growth in the global VoIP and
unified communications market
$90
$80
$70
$60
$50
$40
$30
Example Managed SD-WAN Solution
Source: Webtorials
What are the primary advantages that would drive
your company to implement an SD-WAN?
ue (US$ Billions)
Increase flexibility
Reduce OPEX
Improve application performance
Simplify operations
Improve security
Improve availability
Deploy new functionality more quickly
Add bandwidth more quickly
Provide better visibility
Reduce CAPEX
MPLS only
~$2,520,0 0
Hybrid
~$1,200,000
Dual Internet
~$264,000
~$220/Month
MPLS - 5Mbps
Internet 10 Mbps
Internet 10 Mbps
Monthly Cost P
Cost Per Year for 100 Sites
OFFICE BRANCH
APPLICATION
TRAFFIC
APPLICATION
ACCELERATION
ROUTER
FIREWALL
INTERNET
IP VPN
DATA CENTER
IP
16%
13%
12%
12%
10%
9%
8%
8%
7%
5%
0% 2% 4% 6% 8% 10% 12% 14% 16%
(Continued on page 90)
28
Channel
Vision
|
September - October, 2016